A knowledge of FIBCs
01.Basic knowledge of flexible container bag
Flexible container bag is an abbreviation of "Flexible Container Bags", but it is generally called "flexible bag" or "flexible".
As the name suggests, it is made of soft material and can be folded small when not in use. The shape of the FIBC bag is mainly round and square, and a heavy lifting strap (hanging rope) is attached to the top of the bag, and can be lifted by a crane.
In addition to the upper inlet, many types also have a lower outlet, so there is no need to turn over the FIBC bag when discharging.
FIBC bags are widely used for efficient transportation and storage and lower costs.
Our company handles decontaminating flexible container bags, weather resistant flexible container bags, UN specification flexible container bags, flexible container bags that support unit flexible containers and units, and halal certification, so it handles flexible container bags that can be used with confidence for Islamic customers.
Our flexible container bag products
Flexible container bags are widely used from the viewpoint of cost reduction and efficiency of transportation and storage.
02.Characteristics of our flexible container bag
Basic part
01
Raw material: Polypromylene (PP) resin
02
Weight: Generally 4kg or less per bag
03
Capacity: Generally 1 cubic meter
04
Filling mass: Generally 300kg-1000kg
Special processing
01
Moisture prevention processing
In order to prevent moisture from entering the flexible container bags, we attach an inner bag(*1) or laminate the flexible container bag(*2).
*1 Inner bag: A PE bag set inside the flexible container bag.
*2 Laminating: PE coating on the flexible container bag.02
Leak prevention processing
In order to prevent the filled powder from leaking from the seams of the flexible container bags, we attach an inner bag, or sew a nonwoven fabric on the seams of the flexible container bags.
03
Antistatic processing
In order to prevent the generation of static electricity during filling, the inner bag or outer bag must be processed with an antistatic agent kneading resin.
04
Conductive processing
Conductive original fabric can be expected to have an extremely high discharge effect compared to ordinary flexible container bags, and they are used for bags containing highly flammable substances. They are mainly divided into the following two types.
1. Conductive laminating fabric: Original fabric made of PP yarn and laminated on both sides with carbon kneading resin.
2. Conductive fiber original fabric: Original fabric in which carbon fibers are woven at equal intervals on the warp of PP yarn.
※Surface resistance value:Normal lamination fabric
Conductive lamination fabric
Conductive fiber original fabric
Antistatic processing
Surface leakage resistance(Ω) 1.0×1015 or more
6.7×105 or less
1.0×107 or less
1.0×108-10
Surface leakage resistance(Ω)
Normal lamination fabric
1.0×1015 or more
Conductive lamination fabric
6.7×105 or less
Conductive fiber original fabric
1.0×107 or less
Antistatic processing
1.0×108-10
05
UV protection processing
To use of UV inhibitor kneading resin for the body material of flexible container bags.
*Flexible container bags made of PP original fabric may deteriorate rapidly when exposed to ultraviolet light, and make them unusable. Therefore, outdoor use should be avoided in principle.06
Transport of Dangerous Goods (UN) Flexible Container Bags
Flexible Container bags that can respond to the UN Recommendations on the Transport of Dangerous Goods. It is necessary to conduct a performance test of the flexible container bags by a public testing organization. You can check our flexible container bags conforming to the UN standard, from this page.
03.Structure of flexible container bags
Flexible container bags are mainly composed of the main body, input port, discharge port, hanging parts, etc. Please refer to the image below.
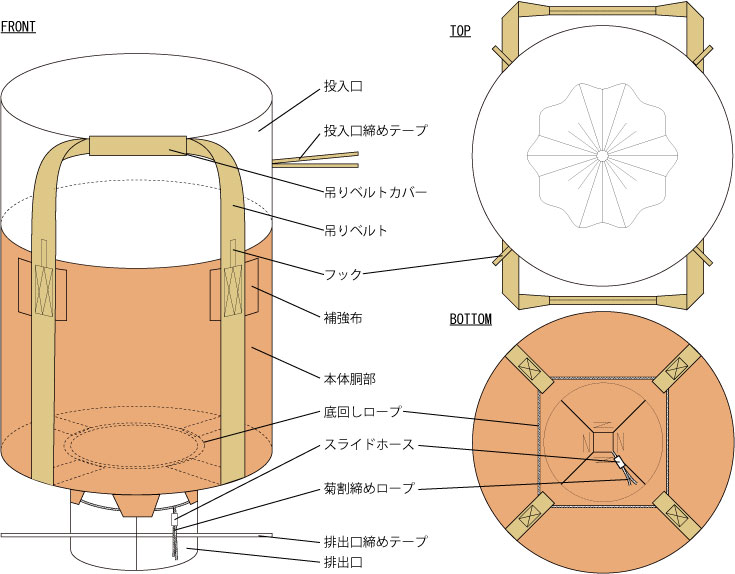
04.Manufacturing process of flexible container bags
01
From raw material to yarn: We make yarn for flexible container bags from raw material PP.
02
From yarn to fabric: The fabric of the flexible container bags are woven by a special loom.
03
From fabric to bag: We sew the finished fabric and make it into a bag. In addition, we take time to inspect the quality.
04
Packing and Shipping: Fold it compress, and ship it.

Raw material PP

Yarning

Weaving

Sewing

Inspection

Packing
05.JIS standard for flexible container bags
JIS Z 1651: 2017 test standards
Type | Performance | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
Repeating the top lifting test | Compression and stacking test | Drop impact test | ||
Repetitive load | Final load | |||
| Running I type | 6×SWL | 8×SWL | In case of two stacking stages | SWL×Fall height(0.8m) |
| Running J type (class 1, class 2) | 2×SWL | 5×SWL | ||
| Cross standard type | 4×SWL | 6×SWL | ||
| Cross single type | 2×SWL | 5×SWL | ||
Running I type
Repeating the top lifting test
Repetitive load:6×SWL 70 cycles
Final load:8×SWL 1 time
Compression and stacking test
In case of two stacking stages:4×SWL 6 hours
In case of 3 or more stacking stages:N(stacking stages)×1.8×SWL 6 hours
Drop impact test
SWL×Fall height(0.8m)
Running J type (class 1, class 2)
Repeating the top lifting test
Repetitive load:2×SWL 70 cycles
Final load:5×SWL 1 time
Compression and stacking test
In case of two stacking stages:4×SWL 6 hours
In case of 3 or more stacking stages:N(stacking stages)×1.8×SWL 6 hours
Drop impact test
SWL×Fall height(0.8m)
Cross standard type
Repeating the top lifting test
Repetitive load:4×SWL 70 cycles
Final load:6×SWL 1 time
Compression and stacking test
In case of two stacking stages:4×SWL 6 hours
In case of 3 or more stacking stages:N(stacking stages)×1.8×SWL 6 hours
Drop impact test
SWL×Fall height(0.8m)
Cross single type
Repeating the top lifting test
Repetitive load:2×SWL 30 cycles
Final load:5×SWL 1 time
Compression and stacking test
In case of two stacking stages:4×SWL 6 hours
In case of 3 or more stacking stages:N(stacking stages)×1.8×SWL 6 hours
Drop impact test
SWL×Fall height(0.8m)
*SWL = Safe Working Load.
Type | Performance | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Weatherability | Water resistance | Heat resistance | Cold resistance | Crumple resistance | |||
Method A | Method B | Method C | |||||
| Running I type | 200 hours survival rate – 50% or more | 200 hours survival rate – 80% or more | 200 hours survival rate – 70% or more | 25 hours survival rate – 85% or more | 1kg load at 70°C for 1 hour | 1kg load at -25°C for 1 hour | 9.8N |
| Running J type (class 1, class 2) | 200 hours survival rate – 70% or more | 200 hours survival rate – 85% or more | 200 hours survival rate – 75% or more | ||||
| Cross standard type | 200 hours survival rate – 50% or more | 200 hours survival rate – 80% or more | 200 hours survival rate – 70% or more | 9.8N | |||
| Cross single type | |||||||
Running I type
Weatherability
Method A:200 hours survival rate – 50% or more
Method B:200 hours survival rate – 80% or more
Method C:200 hours survival rate – 70% or more
Water resistance
25 hours survival rate – 85% or more
Heat resistance
1kg load at 70°C for 1 hour
Cold resistance
1kg load at -25°C for 1 hour
Crumple resistance
9.8N 1,000 times
Running J type (class 1, class 2)
Weatherability
Method A:200 hours survival rate – 70% or more
Method B:200 hours survival rate – 85% or more
Method C:200 hours survival rate – 75% or more
Water resistance
25 hours survival rate – 85% or more
Heat resistance
1kg load at 70°C for 1 hour
Cold resistance
1kg load at -25°C for 1 hour
Crumple resistance
9.8N 1,000 times
Cross standard type
Weatherability
Method A:200 hours survival rate – 50% or more
Method B:200 hours survival rate – 80% or more
Method C:200 hours survival rate – 70% or more
Water resistance
25 hours survival rate – 85% or more
Heat resistance
1kg load at 70°C for 1 hour
Cold resistance
1kg load at -25°C for 1 hour
Crumple resistance
9.8N 200 times
Cross single type
Weatherability
Method A:200 hours survival rate – 50% or more
Method B:200 hours survival rate – 80% or more
Method C:200 hours survival rate – 70% or more
Water resistance
25 hours survival rate – 85% or more
Heat resistance
1kg load at 70°C for 1 hour
Cold resistance
1kg load at -25°C for 1 hour
Crumple resistance
9.8N 200 times
※JIS Z 1651: In 2017, the method is divided into A method, B method, and C method according to the type of weather resistance tester, and the standards are different.
- Method A: Weather resistance test with UVB lamp.
- Method B: Weather resistance test with sunshine carbon arc lamp.
- Method C: Weather resistance test with xenon lamp.
